Two http endpoints are provided by aws-runas to mimic services exposed by AWS to retrieve credentials when running within the walls of AWS infrastructure. The EC2 metadata service is a stripped down version of the EC2 instance metadata service available on EC2 hosts. It exposes the interfaces necessary to retrieve credentials, but not the other paths exposing other EC2 instance information. A service which is similar to the ECS credential service is also available in aws-runas to expose a service which vends AWS credentials to processes on the local system. For either service, instead of credentials for an EC2 instance profile (in the case of the EC2 metadata service), or ECS task roles (in the case of the ECS credential service), aws-runas will serve the assume role credentials of the provided profile.
This will enable use cases where it is cumbersome to setup the execution environment to use aws-runas in the traditional “wrapper” mode. A common scenario for this is developing and executing code in an IDE which needs to obtain credentials to interact with AWS services.
EC2 Metadata Service
The EC2 metadata service can operate in two modes. The 1st is the “legacy” mode, which configures an IP address on the system at 169.254.169.254 and listens for HTTP requests on port 80. This mode requires administrator/root authority to run, as that type of configuration requires privileged access. A 2nd mode is available which does not require administrative level access to run, and should be compatible with most AWS SDK libraries available since 2019.
When running the EC2 metadata service on Linux using sudo, you may need to specify additional flags with the sudo command
in order to carry certain environment variables into the sudo environment. If you see log output saying ‘an AWS
region is required, but was not found’, and it is trying to load the AWS config file from root’s home directory, add the
--preserve-env=HOME or the -E flag to the sudo command. For example:
sudo --preserve-env=HOME aws-runas serve ec2 my-profile
The EC2 metadata service supports access via the IMDS v1 and v2 APIs. The v2 API implementation does not implement the full security measures of the actual AWS interface, merely enough to satisfy the requests so credentials can be returned.
More information on the AWS EC2 instance metadata service can be found in their documentation
Running the service
To run the EC2 service in the privileged mode, call the command without the -p command-line argument, like so:
aws-runas serve ec2 my-profile
To run the service in the un-privileged mode, use the -p flag to configure a specific port for the service to listen on:
aws-runas serve ec2 -p 8000 my-profile
Configuring programs to use the service
For either mode of the EC2 service, you will need to set an environment variable, so the program will communicate with
the service. For most programs the environment variable is AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE, for programs based on the Java
SDK the environment variable is called AWS_CREDENTIAL_PROFILES_FILE. For example:
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE=/dev/null aws s3 ls
When using the un-privileged mode (via the -p option), an additional environment variable called
AWS_EC2_METADATA_SERVICE_ENDPOINT must be set to the local endpoint URL of the service, which is shown in the output
when the service is started. Using the example above to run the service on port 8000:
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE=/dev/null AWS_EC2_METADATA_SERVICE_ENDPOINT='http://127.0.0.1:8000/' aws s3 ls
Important Note
When using a non-IAM (SAML/Web Identity) profile with the EC2 metadata service, you may encounter timeout issues when
using the awscli. This is due to the default timeout for the awscli EC2 metadata interaction of 1 second. In some
cases, the need to communicate with the identity provider before fetching the AWS role credentials will cause this awscli
timeout to be exceeded. To work around this issue, you can set either (or both) of these parameters in your .aws/config
file: metadata_service_timeout or metadata_service_num_attempts.
For more information see the AWS docs
ECS Metadata Service
Unlike the EC2 metadata service, the ECS metadata service does not require any additional permissions to run, since it listens on a non-privileged port on an existing network interface.
Running the service
By default, (without the -p command-line argument) the ECS service will listen on port 12319. To change the port number,
use the -p command-line argument.
aws-runas serve ecs -p 8888 my-profile
Configuring programs to use the service
To allow the program to communicate with the service 2 environment variables must be configured. The first configures
the endpoint URL for the service, and is called AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_FULL_URI. The other environment variable is
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE; for programs based on the Java SDK the environment variable is called
AWS_CREDENTIAL_PROFILES_FILE. For example:
AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_FULL_URI='http://127.0.0.1:12319/credentials' \
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE=/dev/null aws s3 ls
The ECS credential service of aws-runas also supports appending an alternate profile name to the endpoint URI to retrieve
credentials for other profiles without having to run an additional service, or stop and restart the running service. In
the following example, credentials will be retrieved for a profile named other-profile instead of the profile the service
was started with.
AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_FULL_URI='http://127.0.0.1:12319/credentials/other-profile' \
AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE=/dev/null aws s3 ls
Browser Interface
Every mode of the metadata credential service provides a browser-based interface for configuring the profile to use, as well as handling multi-factor authentication and username/password authentication to external identity providers. The interface can be accessed at the following URLs:
- Privileged EC2 endpoint: http://169.254.169.254
- Unprivileged EC2 endpoint: http://127.0.0.1:NNNN (where NNNN is the port set via the
-poption) - ECS endpoint: http://127.0.0.1:12319 (by default, set port as necessary when using the
-poption)
There is only a single screen available in the interface, shown below:
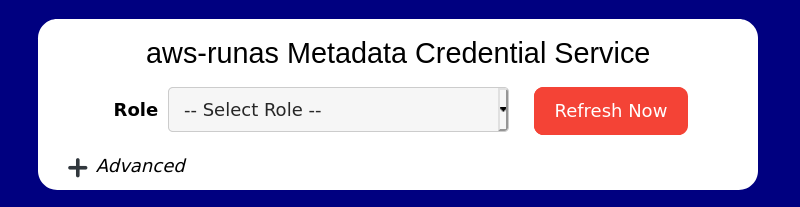
The ‘Role’ drop down will contain a list of roles available in the .aws/config file to select from. Choosing a role from the list will automatically switch the active role in the service, there is no requirement to submit or refresh after selecting a role from the drop down list.
The ‘Refresh Now’ button is not used as part of the normal workflow in the browser interface. It is provided as a way to refresh the credentials used for the role in case there are errors retrieving credentials through the service. If the current set of credentials has expired, you may be required to re-authenticate (for configurations using SAML and OIDC), and you may be prompted to provide the MFA code.
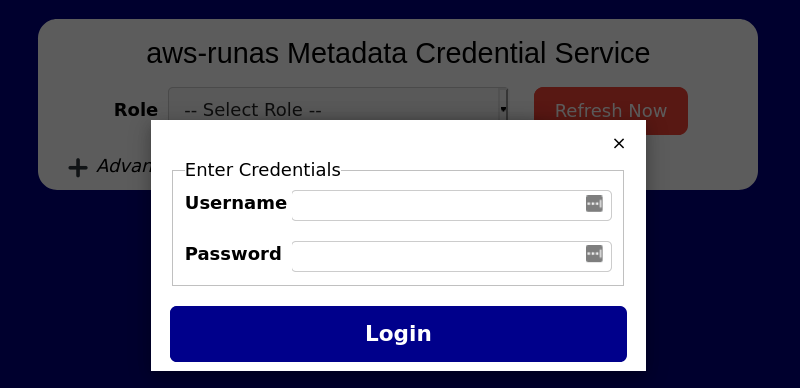
For roles using SAML or OIDC authentication, you may be prompted to enter the credentials for your identity provider if a valid session can’t be found, and the credentials are not set in the config files. The dialog will appear similar to the following screenshot…
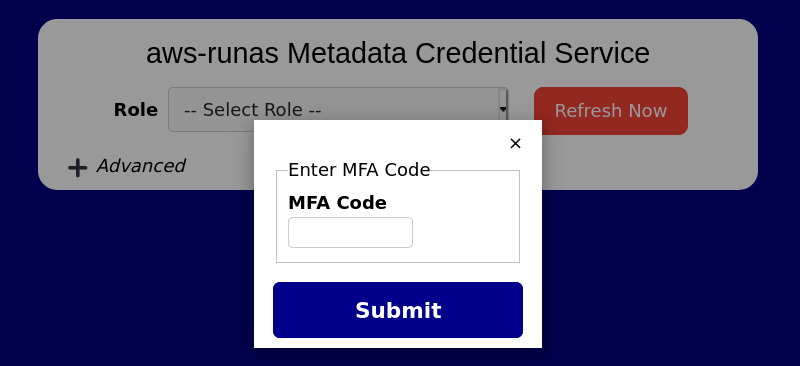
If supplying a multi-factor authentication code is required for the IAM role or your identity provider, you will receive a popup dialog for you to enter your MFA code. The dialog will appear similar to the following screenshot…
HTTP API
The EC2 and ECS service endpoints expose common HTTP endpoints which allow configuration of the service to happen outside the browser.
GET /list-profiles
List profiles found in the .aws/config file. Returns a JSON array of profiles in the .aws/config file which do not have
the role_arn attribute, indicating it is a potential candidate for use as a source_profile
GET /list-roles
List roles found in the .aws/config file. Returns a JSON array of profiles in the .aws/config file which contain the role_arn attribute.
GET /profile
Returns a JSON object containing details about the active profile (set at start up, via the browser interface, or
using POST /profile)
POST /profile
Updates the active profile used for retrieving credentials. The request body is a string containing the name of the profile in the .aws/config file having the role you wish to obtain credentials for. If successful, returns a JSON object with the profile details.
If accessing the profile requires additional authentication (MFA or username/password), this endpoint will return a
HTTP 401 (Unauthorized) status with a X-AwsRunas-Authentication-Type header indicating the type of authentication
required. (AUTH for username/password authentication or MFA for multi-factor authentication code)
POST /auth
Supplies additional username/password authentication information in order to obtain credentials for a profile. The
incoming data is expected to be an HTTP POST with a content type of application/x-www-form-urlencoded having the form
fields username and password containing the necessary credentials to authenticate to the identity provided used with
the role.
POST /mfa
Supplies the multi-factor authentication code in order to obtain the credentials for a profile. The incoming data is
expected to be an HTTP POST with a content type of application/x-www-form-urlencoded having the form field mfa
containing the necessary code needed to get credentials for the role.
GET /latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/
Part of the EC2 instance metadata API. On a real EC2 instance this would return the instance profile associated with the instance. With aws-runas this returns the name of the active profile as a string.
GET /latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/<profile>
Part of the EC2 instance metadata API. The <profile> path argument is the name of the active profile. On a real EC2
instance this would return the credentials for the instance profile associated with the instance. With aws-runas this
returns the credentials for the active profile as a JSON object in the form expected by the EC2 metadata service.
GET /credentials
Part of the ECS credentials API. Returns credentials for the active profile as a JSON object in a form compatible with the ECS credential endpoint.
GET /credentials/<profile>
An extension of the ECS credential API. Returns credentials for the profile specified in the <profile> path argument
without changing the active profile.